Making use of a parameter and ‘invoke custom function’ allows you to control the filtering of a Power BI report data source without editing the Power BI file. This method can offer filtering multiple selections at the source and offers end users the option of controlling this filtering from a spreadsheet without the need to call the developer.
Setting up Power BI using Invoke Custom Function
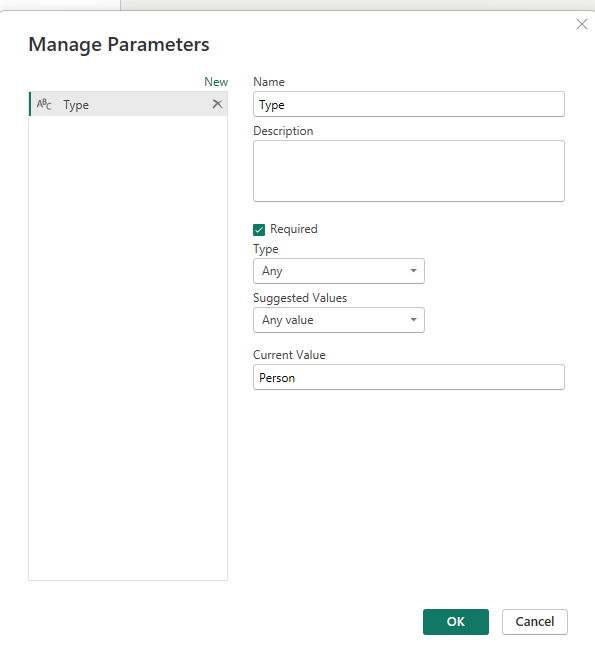
- We will filter on a field called ‘type’, which is used in the v_dim_customer table. Here, we create a parameter called ‘type’ as a text field and give it a current value of ‘Person.’
2. Create a native database query to the SQL Server database, which includes the parameter in the WHERE clause of a SQL statement. Here we create a table from our V_DimCustomer table from the ContosoRetailDW.
let
// Connect to the database
Source = Sql.Database("localhost", "ContosoRetailDW"),
// SQL query with a parameter placeholder
SqlQuery = "SELECT CustomerKey, FirstName, DateFirstPurchase, CustomerType FROM V_DimCustomer WHERE CustomerType = @Type",
Result = Value.NativeQuery(Source, SqlQuery, [Type = Type])
in
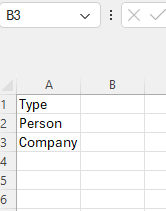
Result3. Create a sheet for importing the options. In a prod environment, you could host this on OneDrive Business, Google Sheets, or SharePoint and import it into the model, so it will refresh in the cloud. I’ve called it ‘ControlTable’ in this example. You could also create a manual table if you want.
 | 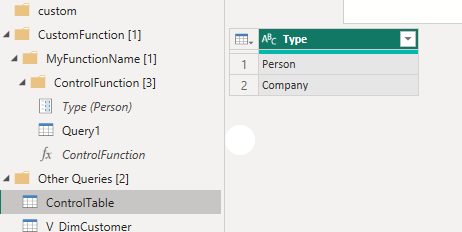 |
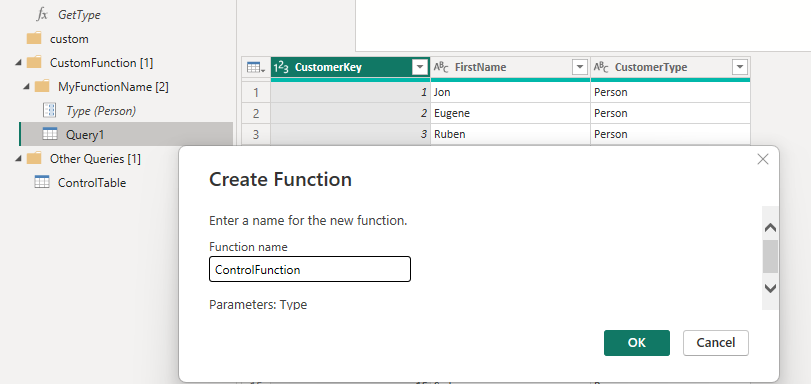
4. In the main native SQL query – right click on the table and select ‘Function’. Give the function a name, and note that it selects the parameter used in the query automatically.
5. Now select the control table and on the ‘Add Columns’ Tab, select ‘Invoke Custom Function’, give it a name, and select the control function created earlier.
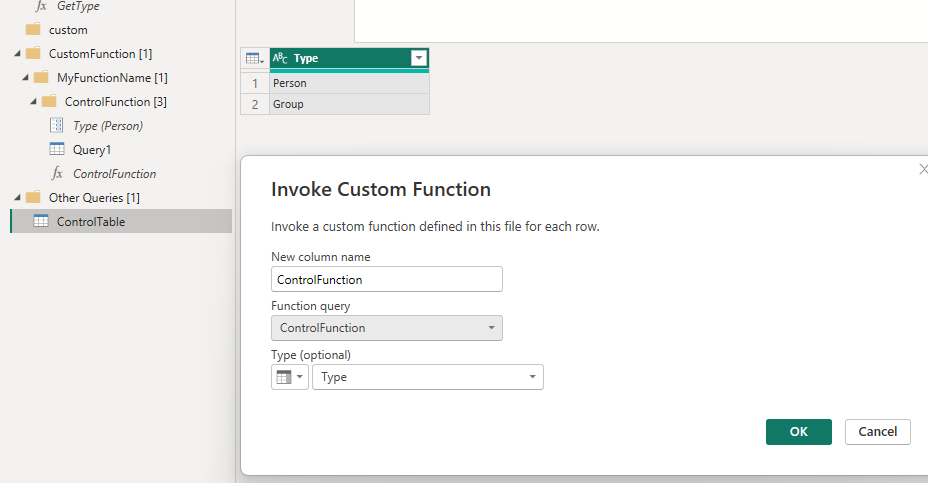
6. Now, on the new columns created for the control function right right-click the 2 arrows and select the desired columns. This will then create a new output using the fields in the Control table to filter the output of the original query, but based on the fields in the spreadsheet, and will therefore update on refresh.
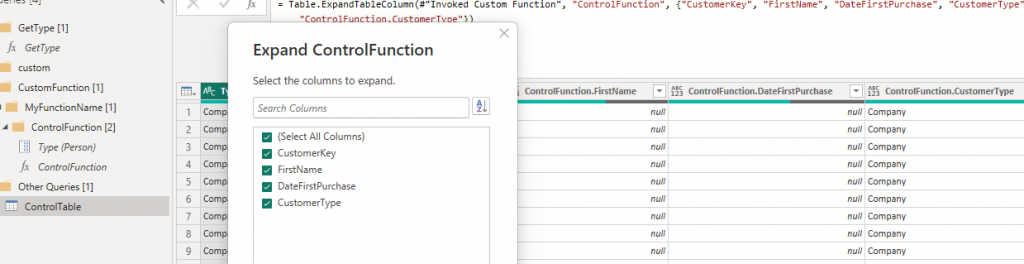
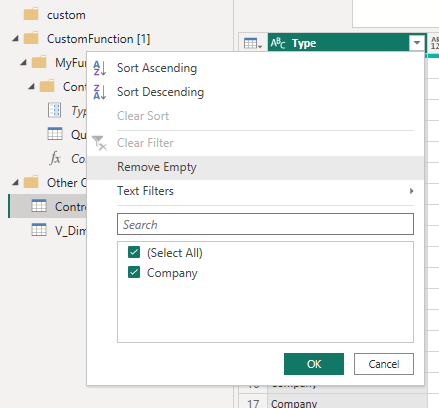
7. Filter the table to check the selections.
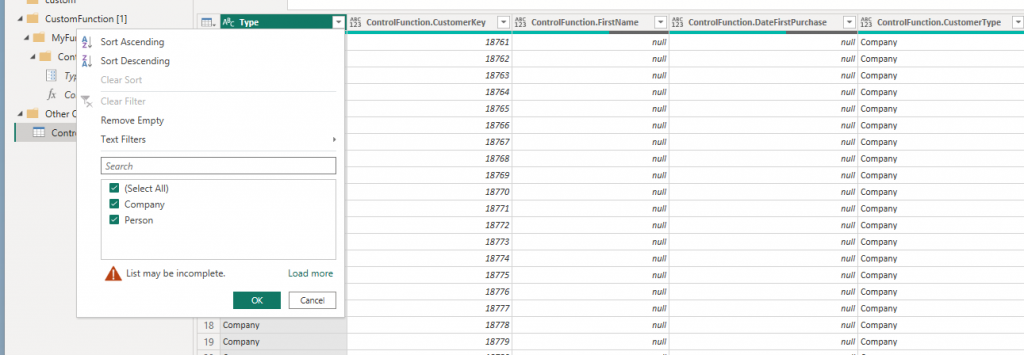
8. Now to test if it all works. In the spreadsheet, change the selection; in this example, select Company only and refresh the data.
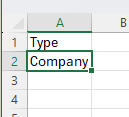
Your data should now be filtered by company.
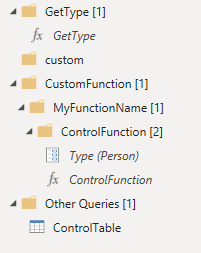
Also of note is that when the custom function table is created, the original query table disappears, but it took a while for Power BI to tidy it up.
For more information on Invoke Custom Function
